Create your own webpage using GitHub pages#
Nate Quarderer, Elsa Culler
Modified Aug 30, 2023
GitHub is a powerful software development tool owned and operated by Microsoft. It is used almost universally for software development and scientific projects. It lets you:
Keep track of all the changes you have ever made, when, and why
Collaborate with others
Get your code online so you can access it anywhere
Use a cloud platform to run your code
Publish a website in minutes We’ll be focusing on that last feature in this activity, in which you will create and publish your own online portfolio website. You can read more about
gitandGitHubin our open Earth Data Science textbook.
Step 0: Create a GitHub account#
Use this link to create a free GitHub account.
Warning
If you already have a GitHub account, there is no need to create a new account!
Step 1: Create a new repository#
Once you have a GitHub account, get started by creating a new repository for your webpage. There are several ways to accomplish this task.
Warning
Sometimes buttons on GitHub are blue instead of green.
What is a repository?
A GitHub repository is a collection of code, documentation, and configuration files. All changes you make in a repository will be tracked using the version control system git. You can discuss and manage your project’s work within the repository.
To do this you can:
Navigate to your profile page
Click on the dropdown arrow next to your profile photo in the upper right corner
Select
Your profile
Select the Repositories tab from the menu near the top of the page.

From here, you can select the green New button on the right to get started.

Customize the settings. You can name your repository anything short and descriptive. We recommend
<yourusername>.github.iobecause it results in the simplest url for your website. You can also: * Give your repository a description * Make your repository Public * You can skip adding the gitignore file for now * Add a README if you like * Choose a License for your repository, if you plan to keep any code in the repository. Check out choosealicense.com for more information about popular options. * Once you’re done, select the green Create Repository button at the bottom of the page
Speak Code
When reading code snippets, the < and > symbols are used to surround text you should replace with something applicable to you and your project. Do not leave the < and > symbols in place!. For example, in this case your repository name might look something like jdoe.github.io, if jdoe was your GitHub username.
Step 2: Create a new index.md file#
You will create a new file called index.md that will serve as the content for your webpage. To do this you can :
Select the Add file button from the menu on the right
Select Create new file.
Name your new Markdown file
index.md. This will make it the home page of your website. Then, add a Markdown header text to your index file, e.g.
# A fabulous Earth Data Science Portfolio
Note
You can change this text to your name or something else. This is your website, and you’ll always be able to come back and make edits!
Step 3: Commit changes#
Now that you’ve created your index.md file and added some text, you’ll want to commit changes to your repository. Add an optional extended description of your changes and then select the green Commit changes button at the bottom of the page.
Step 4: Build your webpage#
Once you’ve created your index.md file you’re ready to build your webpage. From your repository, select the Settings tab from the right end of the menu.

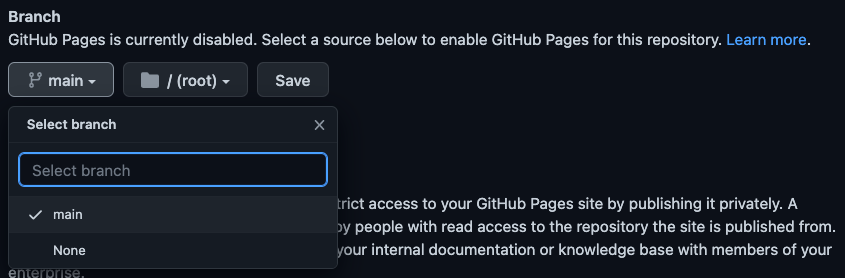
From here, scroll down the menu on the left and select Pages.
Now you’ll want to select the main option under the Branch heading and then select Save.
Step 5: Check on your webpage#
Check in on your webpage to see how it is doing by opening the link https://username.github.io/ in a new tab in your web browser. Here, you’ll need to replace username with your GitHub username. Once you see your name (or whatever text you added to your index.md file in Step 2) appear as a Markdown header, then you know your webpage is working!
Note
Sometimes your webpage can take a minute or so to build so be patient and refresh every 30 seconds or so until the page is done building. You can track the progress in the Actions tab.
Step 6: Start adding information to your webpage#
Now you’re ready to start adding some more information to your webpage. Navigate back to your repository and open the index.md file that you just created. You will edit this page by clicking on the pencil icon on the right of the menu near the top of your repository page on GitHub. You will use Markdown and Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) to add text, links, images, and other content to your webpage. Markdown and HTML are both common markup langauges, and have wide application including formatting text, report writing, and website development.
Here you should think about adding the following information to your webpage:#
A photo of yourself
Your name (as a header) if you haven’t already
A bulleted list of links to your public contact information (email, GitHub account, LinkedIn account, social media accounts, etc.)
Your educational and professional background
A biographical paragraph about yourself
What you’re excited about learning about Earth Data Science
Questions that you’d like to answer using Earth Data Science
Note
You will want to review the Markdown Basic Syntax guide to help you format your webpage using Markdown and HTML. We also have a lesson in our Earth Data Science textbook that may be helpful.
Note
Warning
Always remember to commit changes so that your updated content gets added to your webpage.
Step 7: Add website metadata and theme#
GitHub pages has some build in themes that you can use to make your website more attractive.
To preview themes:
Go to the GitHub theme page
Click on the link to a theme you are interested in. This will take you to the theme repository.
Scroll down in the repository until you see a link like “preview what this theme will look like” at the top of the README file (below the code).
The _config.yml file that you created to add a theme can also be used to change the title of your website from the default (the name of your repository). Check out the README for your theme to see what parameters are available For example, and example _config.yml file for the minimal theme looks like:
title: J. Doe's Awesome Portfolio Website
description: Check out my projects!
logo: img/headshot.png
remote_theme: pages-themes/minimal@v0.2.0
plugins:
- jekyll-remote-theme
So what is YAML?
The _config.yml file is written in YAML, a human-readable format for structured information (lists and key/value pairs). Learn more about YAML on their website
